Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a cornerstone of modern digital marketing. Among the many factors influencing SEO, the URL structure of your website is a critical yet often overlooked element. This guide explores SEO-friendly URLs in detail, offering practical insights to help you optimize your website for search engines and improve user experience.
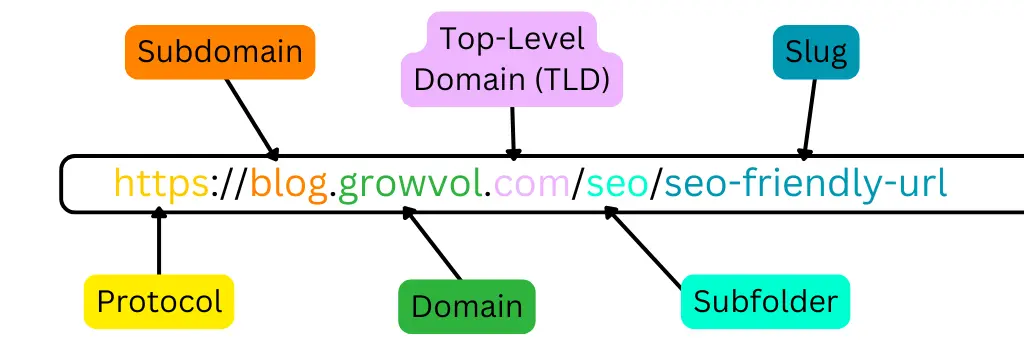
What Is an SEO-Friendly URL?
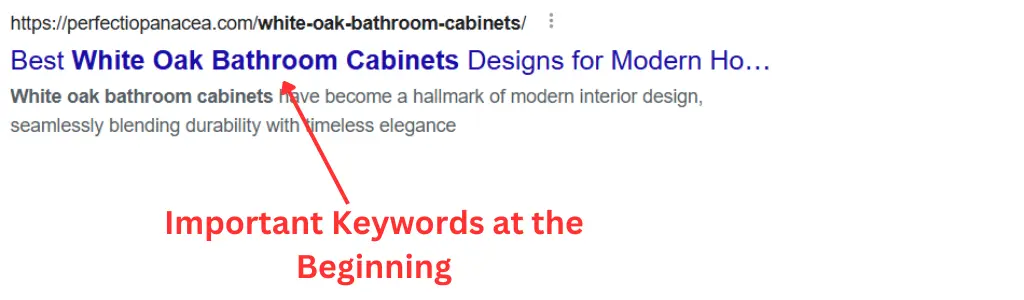
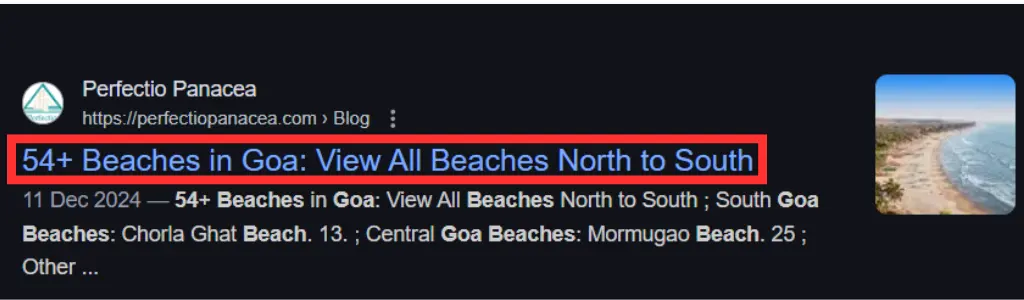
An SEO-friendly URL is a web address designed to meet both user and search engine requirements. These URLs are concise, descriptive, and easy to read, helping search engines understand the page’s content while ensuring users can navigate the website effortlessly.
For example:
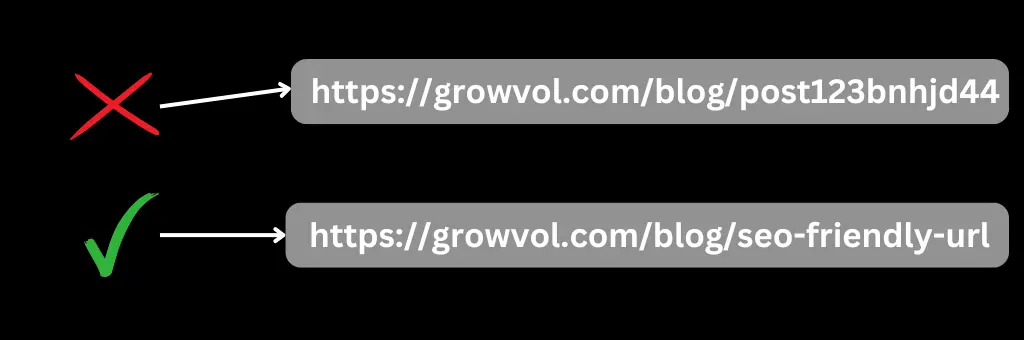
- Non-SEO-friendly:
www.example.com/p=123 - SEO-friendly:
www.example.com/seo-friendly-url-guide
Why Are SEO-Friendly URLs Important?
- Improved User Experience: Descriptive URLs provide users with a clear idea of what to expect on a webpage.
- Enhanced Click-Through Rates (CTR): Clean and relevant URLs attract more clicks, especially in search engine results.
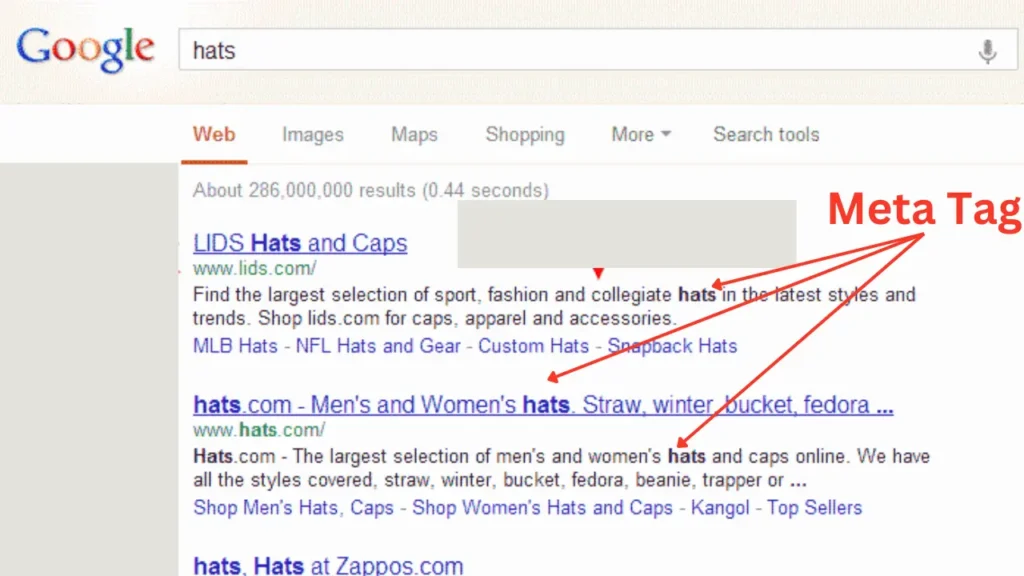
- Better Indexing: Search engines use URLs to understand a page’s content, making proper structuring crucial for indexing.
- Keyword Optimization: URLs containing target keywords can improve rankings for those terms.
- Easy Sharing: Short and meaningful URLs are easier to share across platforms and devices.
Characteristics of an SEO-Friendly URL
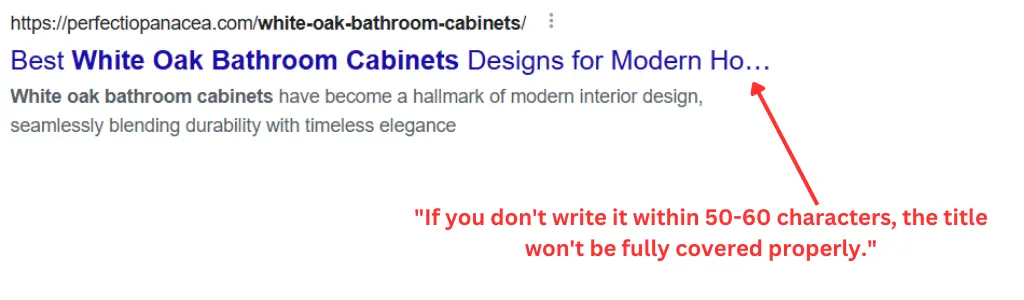
- Short and Simple: Avoid overly long URLs. A concise URL is easier to read and share.
- Descriptive: Clearly indicate the content of the page.
- Keyword-Rich: Include primary keywords naturally.
- Use Hyphens: Separate words with hyphens (
-), not underscores (_). - Lowercase Letters: Always use lowercase to avoid duplicate content issues.
- Static, Not Dynamic: Static URLs are easier for both users and search engines to understand.
- Avoid Special Characters: Exclude characters like
#,@, or%as they complicate readability. - Canonicalization: Ensure there’s only one version of the URL accessible to avoid duplicate content issues.
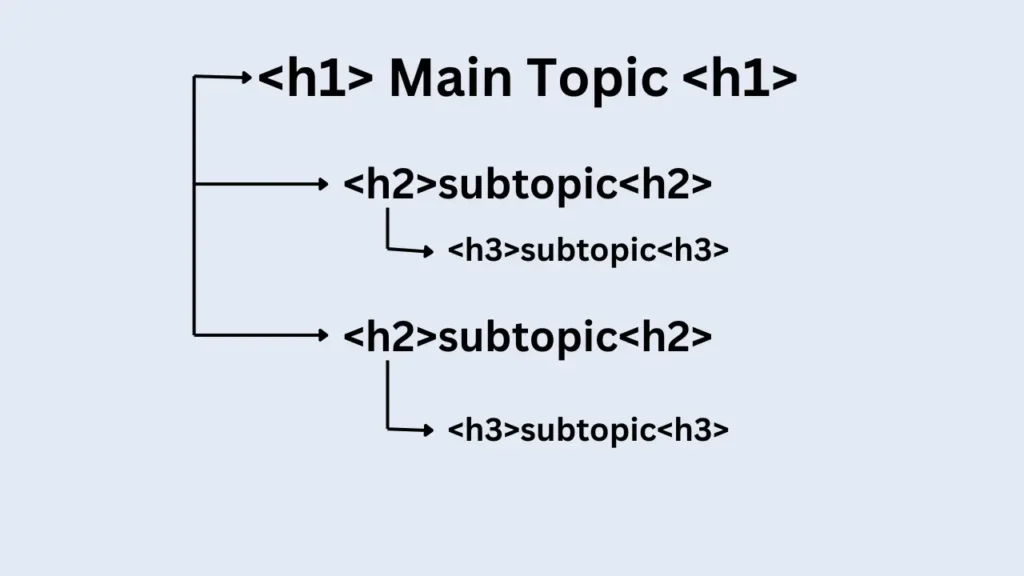
How to Create SEO-Friendly URLs
Plan Your URL Structure
- Use a logical hierarchy that reflects your website’s structure.
- Keep parent categories and subcategories in the URL if applicable.
- Example:
www.example.com/blog/seo-tips.
Incorporate Keywords
- Research relevant keywords using tools like Google Keyword Planner or Ahrefs.
- Place primary keywords in the URL, avoiding overstuffing.
Keep It Short
- Remove unnecessary words like “and”, “but”, or “of”.
- Example: Change
www.example.com/how-to-make-seo-friendly-urls-for-beginnerstowww.example.com/seo-friendly-urls.
Avoid Numbers and Dates
- Exclude dates or version numbers unless absolutely necessary, as they make updating content cumbersome.
Use Hyphens to Separate Words
Avoid underscores or spaces; stick to hyphens to ensure readability.
Implement HTTPS
Google considers HTTPS a ranking signal. Always use secure protocols in your URLs.
Canonicalization
Prevent duplicate content issues by setting a canonical URL for pages with similar content.
Remove Stop Words
Eliminate words like “and”, “the”, or “of” unless absolutely necessary for clarity.
Examples of SEO-Friendly URLs
- Blog Post:
- Bad:
www.example.com/blog/post123 - Good:
www.example.com/blog/seo-friendly-url-tips
- Bad:
- E-commerce Product:
- Bad:
www.shop.com/product?id=5678 - Good:
www.shop.com/mens-running-shoes
- Bad:
- Category Page:
- Bad:
www.example.com/category/xyz - Good:
www.example.com/electronics/smartphones
- Bad:
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overloading URLs with Keywords: Avoid “keyword stuffing” as it can lead to penalties.
- Using Auto-Generated URLs: Dynamic URLs with random strings or IDs harm readability and SEO.
- Ignoring Redirects: Always set up proper 301 redirects when changing URLs to avoid losing traffic and rankings.
- Inconsistent URL Structure: Maintain consistency to prevent confusion for users and search engines.
- Neglecting Mobile Optimization: Ensure URLs are mobile-friendly since Google uses mobile-first indexing.
Tools for Optimizing URLs
- Yoast SEO (WordPress): Helps generate SEO-friendly URLs and provides optimization tips.
- Screaming Frog: Analyzes existing URLs for SEO issues.
- Ahrefs: Provides insights into keyword usage and competitor analysis.
- Google Search Console: Identifies URL issues and suggests improvements.
- URL Rewriting Tools: For developers, tools like Apache’s mod_rewrite can help.
Advanced URL Optimization Tips
- Use Breadcrumbs: Display breadcrumbs in URLs for better navigation and SEO.
- Localized URLs for International SEO: Use country-specific domains or subdirectories for international audiences.
- Example:
www.example.com/ukfor the UK andwww.example.com/usfor the USA.
- Example:
- Pagination: Use proper URL structures for paginated content.
- Example:
www.example.com/blog?page=2.
- Example:
- UTM Parameters: While tracking campaigns, ensure UTM parameters don’t create duplicate content.
- Use canonical tags where needed.
Measuring the Impact of URL Optimization
- Monitor Traffic: Use tools like Google Analytics to track changes in organic traffic.
- CTR Analysis: Check your click-through rates in Google Search Console.
- Rank Tracking: Use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to monitor keyword performance.
- Bounce Rate: A lower bounce rate often indicates user-friendly URLs.
Conclusion
An SEO-friendly URL is more than just a technical element; it’s a vital aspect of your website’s overall strategy. By implementing the tips outlined in this guide, you can create URLs that enhance user experience, improve search engine rankings, and boost overall website performance. Always remember that consistency and simplicity are key to achieving long-term success with SEO-friendly URLs.
By focusing on best practices, avoiding common pitfalls, and leveraging the right tools, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the art of URL optimization.